Australian Huntsman spiders are part of the Family Sparassidae, once known as Heteropodidae. They are hairy spiders often called “tarantulas.” These spiders are famous for hiding behind curtains and suddenly running out, which scares many people. You can often see them on house walls, adding to their fearsome reputation.
Identification
Huntsman spiders are large with long legs. They are mostly grey to brown and sometimes have banded legs.
Many, like Delena, Isopeda, Isopedella, and Holconia, have flattened bodies to fit in narrow spaces like underbark.
Their legs spread out like crabs, giving them the name “giant crab spiders.” Brown Huntsman spiders (Heteropoda species) have mottled brown, white, and black patterns.

Habitat
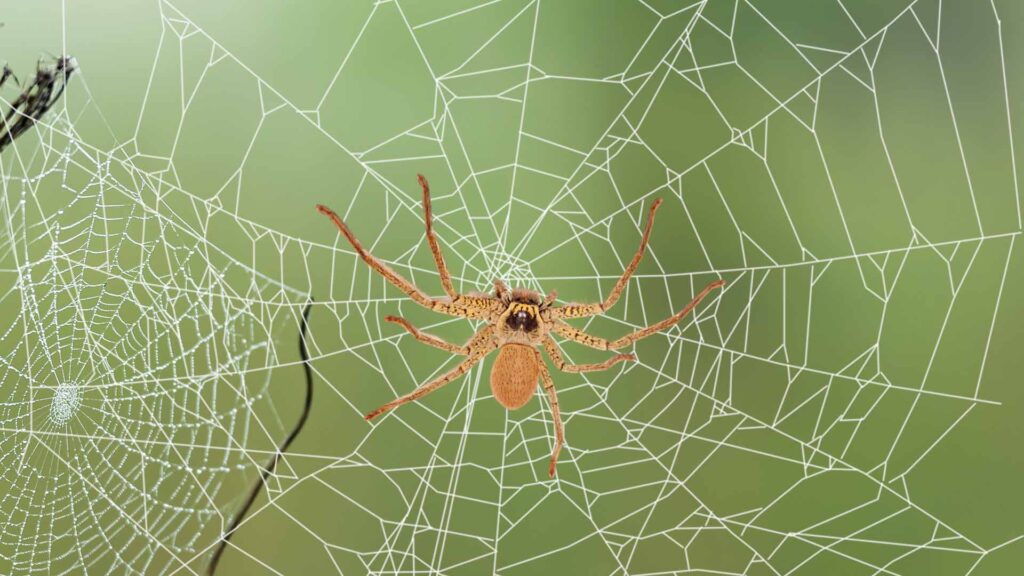

Huntsman spiders live in various natural settings, including:
- Under loose bark on trees
- In crevices on rock walls and logs
- Under rocks and slabs of bark on the ground
- On foliage
The social species, Delena cancerides, is often found in groups under bark on dead trees and stumps, especially wattles. They can also be found on the ground under rocks and bark slabs.
Huntsman spiders of many species sometimes enter houses. They are notorious for entering cars, hiding behind sun visors, or running across the dashboard.
Distribution
Huntsman spiders are widely distributed throughout Australia. However, Heteropoda is mostly absent from Southeastern Australia, and Tasmania has only a few species, notably Delena cancerides and Neosparassus sp.
Huntsman Spider Size
Huntsman spiders are known for their remarkable size and speed, fascinating arachnid enthusiasts and nature lovers. This guide covers various aspects of their size, addressing common queries and providing comparisons with other spider species.
1. General Size of Huntsman Spiders
Huntsman spiders (family Sparassidae) are among the largest spider families in terms of leg span.
Their typical leg span ranges from 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm).
while their bodies measure about 0.7 to 1.4 inches (1.8 to 3.5 cm).

2. Largest Huntsman Spider
The largest species is the Giant Huntsman Spider (Heteropoda maxima) from Laos, which can have a leg span of up to 12 inches (30 cm), making it the largest spider by leg span.
3. Size Comparison with Other Species
- Wolf Spider: Smaller than huntsman spiders, with a leg span of 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 cm). They have more robust bodies.
- Goliath Birdeater: Known as the largest spider by mass, with a leg span of about 11 inches (28 cm) and a body length up to 4.7 inches (12 cm). Comparable leg span but a significantly more massive body.
- Tarantula: Sizes vary, but common species have a leg span of 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm). Larger species, like the Goliath birdeater, can rival the largest huntsman spiders in span.
4. Geographic Variations
- Australian Huntsman Spiders: Species like Holconia immanis can have a leg span up to 9 inches (23 cm).
- Florida Huntsman Spider: Heteropoda venatoria, common in Florida, has a leg span around 5 inches (12.7 cm).
- Korean Huntsman Spider: Typically smaller, with leg spans averaging 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm).
5. Gender Differences
Female huntsman spiders are generally larger than males, especially in body size, a common trait among many spider species.
6. Size Over Lifetime
- Baby Huntsman Spiders: Spiderlings are just a few millimeters upon hatching.
- Growth: They grow through successive molts, shedding their exoskeleton to increase in size over several months to years, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
7. Common Comparisons
- Huntsman Spider vs. Wolf Spider: Huntsman spiders have a larger leg span but smaller bodies.
- Huntsman Spider vs. Tarantula: Some tarantulas match the huntsman in leg span but are more massive.
- Huntsman Spider vs. Goliath Birdeater: The Goliath birdeater is heavier and has a comparable leg span.
8. Visualizing Size
To visualize their size, a fully grown huntsman spider can cover an entire dinner plate with its legs extended, highlighting their substantial size.
Breeding Behaviors
In the genus Isopoda, the mating behavior of Huntsman spiders involves a prolonged courtship:
- The male and female engage in mutual caresses, with the male drumming his palps on the trunk of a tree.
- The male then inserts his palps into the female to fertilize her eggs.
Contrary to some other species, the male is rarely attacked during mating. In fact, many huntsman spiders live peacefully together in large colonies.
For egg-laying and molting, Huntsman spiders often construct silken retreats.
Life History Cycle of Huntsman Spiders
Egg Laying and Guarding
- The female Huntsman spider, such as Isopeda, produces a flat, oval egg sac of white papery silk and lays up to 200 eggs.
- She places the egg sac under bark or a rock and guards it without eating for about three weeks. During this time, the female can be aggressive and will rear up defensively if provoked.
- Some species carry their egg sac under their bodies while moving.
Delena females lay a silk ground sheet, anchor the egg sac to it while laying eggs, then complete the egg sac and pick it up, leaving the ground sheet behind.
Incubation and Hatching
- Incubation periods vary and are influenced by climatic conditions.
- In some cases, like with Isopeda, the female moistens and tears the egg sac open to help the spiderlings emerge.
- The mother stays with her spiderlings for several weeks.
Development and Molting
- Young Huntsman spiders are pale at first and undergo several molts while still with their mother, eventually hardening to a darker brown before dispersing.
- Huntsman spiders molt to grow, and their old skins can often be mistaken for the spider itself when seen on bark or in houses.
Huntsman Spider Bites
Huntsman spiders, known for their large size and impressive speed, are often subjects of curiosity and concern, particularly regarding their bites. This article addresses various aspects of huntsman spider bites, including their appearance, symptoms, pain level, and treatment.
1. Do Huntsman Spiders Bite?
Yes, huntsman spiders can bite humans. However, they are generally not aggressive and will only bite if provoked or threatened. Most bites occur when the spider is accidentally pressed against the skin, such as when moving items where the spider is hiding.
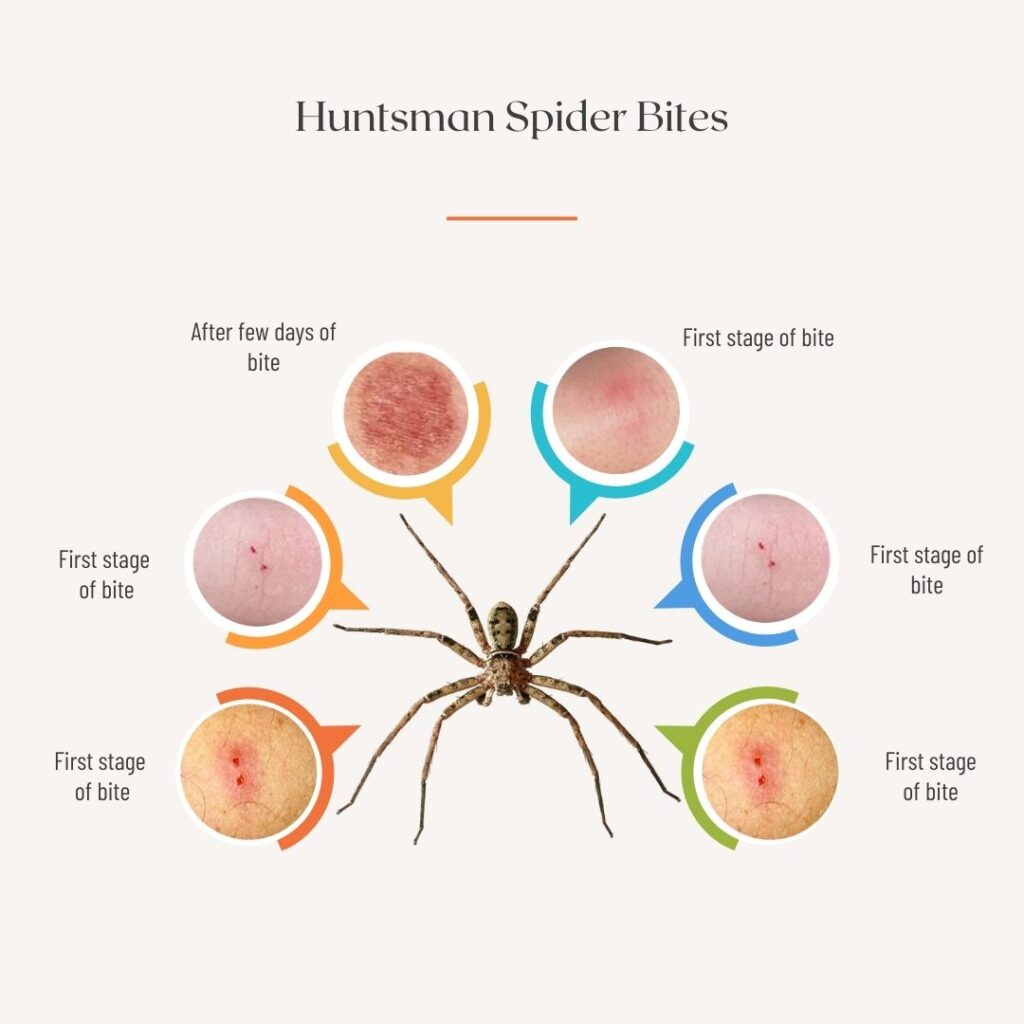
2. What Does a Huntsman Spider Bite Look Like?
A huntsman spider bite typically appears as a small, red, and swollen area on the skin. In some cases, two puncture marks from the spider’s fangs may be visible. The bite site may also develop into a welt or blister in more sensitive individuals.
3. Symptoms of a Huntsman Spider Bite
Common symptoms of a huntsman spider bite include:
- Redness and swelling at the bite site
- Mild to moderate pain
- Itching
- A burning sensation
In rare cases, more severe reactions can occur, such as:
- Nausea
- Headache
- Rapid pulse
- Mild systemic symptoms
4. Pain Level and Duration
The pain from a huntsman spider bite is usually described as mild to moderate and is often compared to a bee sting. The pain typically lasts for a few hours but can persist for up to a day or two. Most people recover fully without any long-term effects.
5. Comparing Huntsman Spider Bites to Other Spiders
- Wolf Spider: Wolf spider bites are also generally non-venomous to humans and cause similar symptoms to huntsman spider bites, including pain, redness, and swelling.
- Black Widow Spider: Black widow bites are significantly more painful and can cause severe symptoms, including muscle cramps, spasms, and systemic effects.
- Brown Recluse Spider: Bites from brown recluse spiders can cause necrotic wounds and require medical attention due to the potential for tissue damage.
6. Treatment for Huntsman Spider Bites
For most huntsman spider bites, home treatment is sufficient. Steps include:
- Cleaning the Bite: Wash the area with soap and water to prevent infection.
- Ice Pack: Apply an ice pack to reduce swelling and numb the pain.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage pain.
- Antihistamines: These can reduce itching and swelling.
If symptoms persist or worsen, or if you experience severe reactions, seek medical attention promptly.
7. Can Huntsman Spider Bites be Dangerous?
Huntsman spider bites are not considered dangerous to humans. They do not possess venom that is harmful to humans, and serious complications are extremely rare. However, allergic reactions can occur, as with any insect bite.
Facts of Huntsman Spider
Impressive Size: Huntsman spiders belong to one of the largest spider families in terms of leg span. Adults can have a leg span ranging from 10 to 12 inches (25 to 30 cm), making them some of the largest spiders in the world.
Unique Mating Rituals: In species like Isopoda, males and females engage in a lengthy courtship involving mutual caresses and palp drumming. Despite the intimate nature of the ritual, males are rarely attacked by females.
Versatile Habitat: Huntsman spiders are adaptable creatures, inhabiting various environments such as under loose bark on trees, in crevices on rock walls, under rocks, and even inside houses and cars.
Social Behavior: Some species of Huntsman spiders, like Delena cancerides, are known for living in large colonies. They can be found sitting together under bark on dead trees and stumps, displaying a surprisingly social behavior for spiders.
Protective Mothers: Female Huntsman spiders demonstrate maternal care by guarding their egg sacs without eating for about three weeks. Some species even carry their egg sacs under their bodies while moving about, ensuring the safety of their offspring.